In a recent publication in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a collaborative research led by the scientist Dr. H. Day, in conjunction with a consortium of researchers, explored the development of allosteric inhibitors targeting SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP2) for cancer therapy.
The methodology included using CacoReady plates to evaluate the in vitro permeability of synthesized SHP2 inhibitors, revealing significant inhibitory activity against cancer cells and suggesting a promising avenue for future anti-cancer drug development.
What are allosteric inhibitors of SHP2?
Allosteric inhibitors of SHP2 constitute a class of compounds designed to modulate the activity of SHP2, a critical regulator of the RAS–MAPK pathway implicated in cancer cell proliferation and growth. By interfering with SHP2 signaling pathways, these inhibitors hold the potential to thwart oncogenic functions.
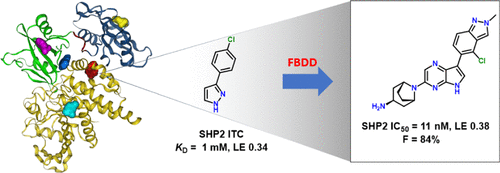
The study, titled “Fragment-Based Discovery of Allosteric Inhibitors of SH2 Domain-Containing Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 2 (SHP2)”, focused on designing and synthesizing a series of allosteric inhibitors targeting SHP2, with particular emphasis on their efficacy in inhibiting SHP2-mediated signaling pathways involved in cancer progression. Among the synthesized compounds, compound 28 exhibited potent inhibitory activity and selectivity against SHP2, warranting further investigation into its therapeutic potential.
Why is it important to determine the permeability of an inhibitor?
Determining the permeability of an inhibitor is crucial to predict its bioavailability, efficacy, and safety, guiding the optimization of compound structure for improved therapeutic outcomes and informing drug delivery strategies. Therefore, assessing in vitro permeability using CacoReady plates was crucial in the research methodology.
The permeability studies revealed varying degrees of cell membrane permeability among the SHP2 inhibitors. This data underscores the need to refine lead compounds’ chemical properties to strike a balance between potency and permeability for optimal therapeutic outcomes.
In summary, this study explores allosteric inhibitors targeting SHP2 for cancer therapy, highlighting the importance of optimizing compound characteristics for efficacy. These findings have promising implications for advancing cancer treatment strategies.
Read full article: Fragment-Based Discovery of Allosteric Inhibitors of SH2 Domain-Containing Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-2 (SHP2), James E. H. Day, et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2024 67 (6), 4655-4675 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02118





