The Caco-2 permeability assay is a crucial in vitro method for evaluating intestinal absortion, empowering researchers to make informed decisions in drug development. If you’re looking to streamline your process while maintaining precision and compliance, understanding this assay is essential.
The primary outcome of such technique is the transport rate of the experimental compound across the Caco-2 monolayer membrane. This positively predicts in vivo absorption across the intestinal system into the bloodstream thanks to the well-established correlation between the in vitro system and the physiologic intestinal absorption.
Our complete Caco-2 Permeability Assay Protocol offers step-by-step instructions, detailed calculations, and expert tips to help you achieve reliable and reproducible results. Want to learn more? Request the full protocol today!
What makes Caco-2 assays essential for drug development?
The Caco-2 cell model has set the standard for evaluating oral drug absorption thanks to its:
- Accuracy: High correlation with human intestinal permeability.
- Versatility: Suitable for passive diffusion, transporter interactions, and efflux studies.
- Regulatory Acceptance: Widely recognized by the FDA and EMA.
By simulating the intestinal epithelial barrier, this model enables researchers to predict in vivo behaviour from in vitro data, saving time and resources during preclinical development.
Assessing intestinal permeability with the specialized Caco-2 permeability assay
The Caco-2 cells incorporated in the CacoReady Kit for permeability assays are seeded on transwell inserts with semi-porous polycarbonate filter providing independent access to both sides of the cell monolayers (donor-receiver or apical-basal compartments) that mimic the intestinal lumen and the blood circulation, respectively. The cells are cultured at 37ºC for 15 days, applying culture medium changes every second day to allow the formation of a confluent monolayer. This cell culture plate has not only been found to be effective for permeability studies, but is also recommended for cytotoxicity assays.
CacoReady can be delivered in 24-well and 96-well/plate with shipping medium, a gel-like cell culture medium established by Readycell, which ensures the viability of Caco-2 cells and enables the transport of cells at room temperature worldwide in a ready-to-use format.
Which are the key steps to perform a successful in vitro permeability assay with CacoReady?
Assessment of cell monolayer integrity
In order to verify that cell integrity meet the standards, Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER), apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) and paracellular flux index (LY) can be assessed. The acceptance criterion after 21 days of differentiation are:
| Measurement | Cacoready® 24w | CacoReady® 96w |
| TEER | > 1000 Ω·cm2 | > 500 Ω·cm2 |
| LY apparent permeability (Papp) | ≤ 1 x 10-6 cm/s | ≤ 1 x 10-6 cm/s |
| LY Paracellular Flux | ≤ 0.5% | ≤ 0.7% |
Test compound permeability assay protocol
CacoReady allows conducting permeability assays (apical to basal or basal to apical) of established or unknown compounds to predict their absorption and interaction with membrane-associated proteins (MDR1-Pgp and BCRP). We recommend to perform the assay for 2h and assess each compound in triplicate in the A-B/B-A directions at initial 10 µM concentration suggested for unknowns.
Compounds concentration may be analyzed by mass spectrometry according to the suitable analytical procedures.
Reference Compounds for Permeability Studies
Several compounds can be used as control tests; the main recommendation is to validate the assay using a high permeable molecule, such as Propanolol, and a low permeability compound, such as Atenolol, in triplicates for each group.
| Low permeability substrate | High permeability substrate | MDR1 (Pgp) substrate | MDR1 (Pgp) inhibitor | BCRP substrate | BCRP inhibitor |
|
Atenolol (10µM) |
Metoprolol (10µM) |
Digoxin (10µM) |
Verapamil (10µM) |
Prazosin (1µM) |
Ko143 (1µM) |
Evaluation of the Compound Permeability
The apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) is calculated from the permeation rate and compound concentration at t=0h and t=2h.
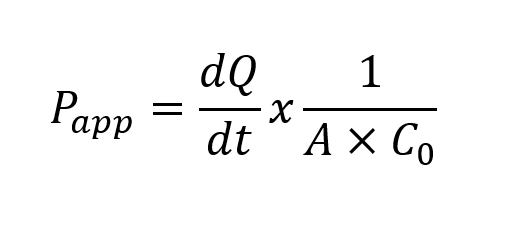
Where:
dQ/dt: amount of product present in the basal (A-B) or apical (B-A) compartment as a function of time (nmol/s).
A: area of transwell (cm2).
C0: initial concentration of product applied in the apical (A-B) or basal (B-A) compartment (nmol/ml).
In vivo Absorption extrapolation
Based on in vitro/in vivo correlation studies, Papp values obtained from Caco-2 barrier studies are used to define and predict the intestinal permeability of the tested compounds.
| In vitro Papp values | Range of predicted in vivo absorption |
| Papp ≤ 10-6 cm/s | Low (0-20%) |
| 10-6cm/s < Papp ≤ 10 x 10-6 cm/s | Medium (20-70%) |
| Papp > 10 x 10-6 cm/s | High (70-100%) |
Learn more
To learn more about the cell models used in permeability testing, as well as the products indicated for the permeability assay protocol, you can consult the following web page.
In case it is required more specific information related to Caco-2 permeability studies and CacoReady kits, you can contact us through our form or sending an email at reagents@medtechbcn.com