This November 2023, the prestigious European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry published a collaborative study led by scientist Davide Moi in affiliation with the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Italy. Under the title “Discovery of Potent HDAC Inhibitors for Targeting Advanced Prostate Cancer,” the article presents the findings on the potential of HDAC inhibitors for treating advanced prostate cancer.
This research also integrated CacoReady plates to assess the in vitro permeability of the HDAC inhibitors. The results revealed promising activity against prostate cancer cells, suggesting a possible approach for future treatment strategies.
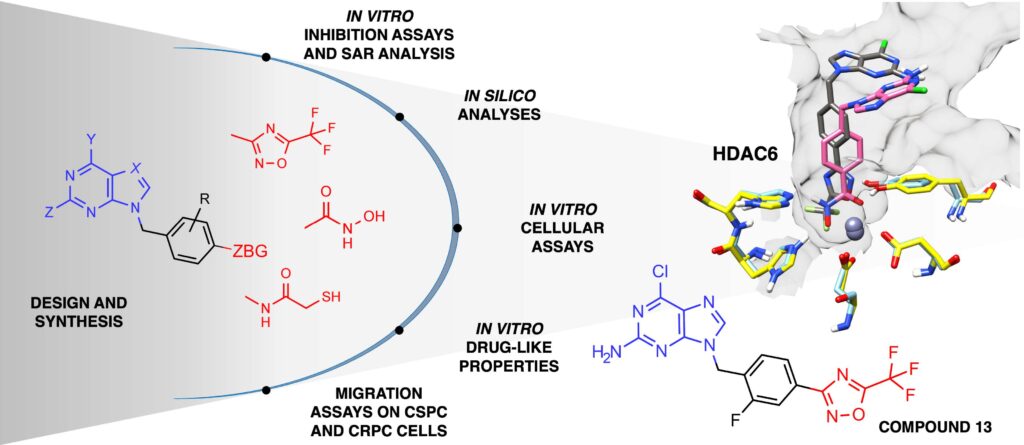
Design of innovative HDAC inhibitors targeting HDAC6 activity.
HDACs (histone deacetylases) are crucial in regulating gene expression by acetylation/deacetylation of lysine residues in histones and non-histone proteins. They are involved in various cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, differentiation, and apoptosis. In the context of prostate cancer, HDACs are particularly interesting because they modulate the activity of the androgen receptor (AR), which is a key driver of prostate cancer progression and drug resistance.
The study aimed to design and synthesize new HDAC inhibitors across three distinct series, emphasizing HDAC6 inhibitory activity. Therefore, the compounds were evaluated for their impact on aggressive prostate cancer cell proliferation, tumor selectivity, anti-migration properties, and in vitro drug-like characteristics.Among the compounds synthesized, compound 13 stood out, identified as a promising lead for future research, since it presented higher selectivity and low toxicity.
Assessing In Vitro permeability: the role of Caco-2 cells
Evaluating in vitro permeability with CacoReady plates was central to the study design. By quantifying the permeability of the synthesized compounds within Caco-2 cells, researchers could identify and select which compounds were best in terms of cellular adsorption.
These results revealed variations in cell membrane permeability among the series of compounds. This observation indicated a possible trade-off between higher in vitro HDAC6 inhibitory activity and lower cell permeability. Consequently, it was concluded that an optimization of the lead hydroxamic acid derivatives is needed to achieve a balance between in vitro potency and cell permeability.
In conclusion, this study provides a nuanced exploration of the potential of HDAC inhibitors in the field of advanced prostate cancer treatment. Furthermore, it highlights the contribution of advanced cell culture products such as Readycell. The results suggest that HDAC inhibitors could play an essential role in shaping the future of prostate cancer therapy, extending the impact of this research beyond its immediate scope.





