Drug-drug interactions are the most common cause of adverse events during clinical stages in polymedicated patients. Alterations in drugs’ metabolism due to unexpected molecular interactions affect significantly compounds’ pharmacokinetics.
The scientific community agrees that two of the main concerns of drug-drug interactions are (a) the increase of active principles in certain tissues that can reach toxicological levels, and (b) metabolism alterations that reduce the expected mechanism of action.
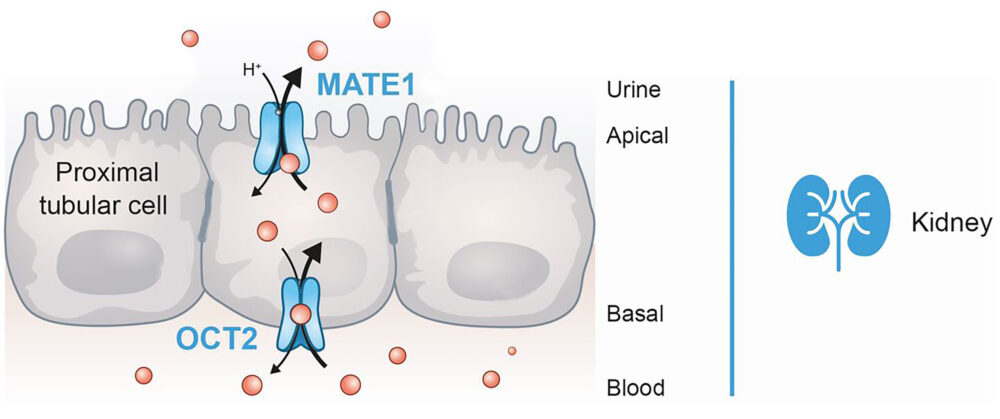
In pharmacological terms, optimal excretion routes are required to prevent these adverse events. Uptake transmembrane receptors, which are mainly expressed in hepatocytes and kidney epithelial cells, have an essential function regulating the elimination of compounds from the blood to the bile and urine.
OCT2 and MATE1 receptors are relevant membrane-bound transport proteins that regulate the renal and hepatic excretion of drugs in synergy with other receptors, such as MATE-2K. When a xenobiotic inhibits the OCT2 and/or MATE1 transporter, drugs excretion entails a significant metabolic increase in the inner cell concentration, thus enhancing the possibility of adverse events due to a possible compound’s toxicity.
Main regulatory agencies recommend in their guidelines investigating uptake receptor interactions for novel compounds during preclinical trials. In vitro models with genetically modified cell lines that overexpress these transporters allow to determine transporter-mediated transmembrane protein interactions, which helps to depict the novel compounds pharmacokinetic profile and obtain additional assessment whether the sponsor should conduct in vivo studies in later stages.
| Inhibitions studies | Substrate studies | |||||||
| FDA | EMA | PMDA | EMA | FDA | PMDA | |||
| MATE1 Transporter | Obligatory | Recommended | Obligatory | Recommended | Obligatory* | Recommended | ||
| OCT2 Transporter | Obligatory | Obligatory | Obligatory | Recommended | Obligatory* | Obligatory* | ||
ReadyCell developed PreadyTake in vitro kits based on transfected HEK 293 cells to assess receptor-mediated interactions with relevant uptake transmembrane receptors that study renal pharmacology.
- PreadyTake MATE1, seeded with HEK293 cells transfected with SLC47A1 gene, overexpressing MATE1 receptor.
- PreadyTake OCT2, 96 wells kit with transfected HEK293 cells, overexpressing OCT2 receptor.
PreadyTake kits are shipped worldwide thanks to ReadyCell’s patented Shipping Medium biotechnology, which assures HEK293 cells viability up to 5 days.
For additional scientific discussion related to drug-drug interaction in preclinical stages, contact our scientists at reagents@medtechbcn.com